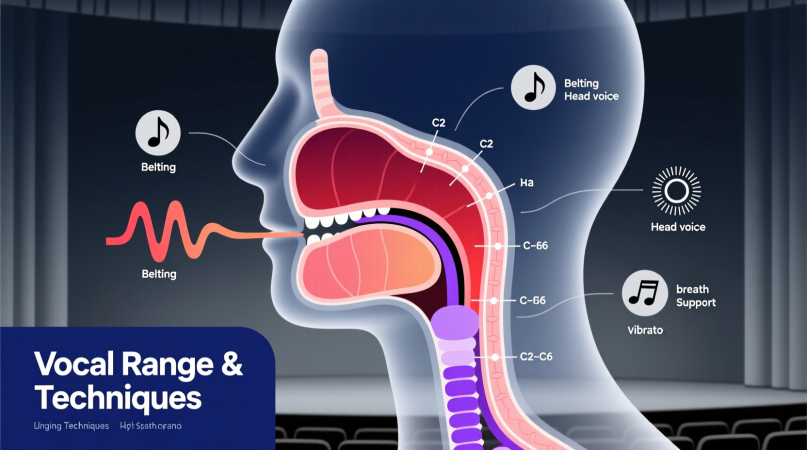
Your vocal range is the span between your lowest and highest comfortable notes. Most singers cover 2–3 octaves, while exceptional voices can stretch much further. By using proven singing techniques—like warm-ups, register blending, and resonance control—you can expand your range safely and sing with more confidence.
What Is Vocal Range?
Vocal range is measured in notes, from the lowest pitch you can produce to the highest. It’s often linked to voice types:
- Bass – E2 to E4 (deepest male voice)
- Baritone – A2 to A4
- Tenor – B2 to A4 (higher male voice)
- Alto – F3 to F5 (lower female voice)
- Mezzo-soprano – A3 to A5
- Soprano – C4 to C6 or higher (highest female voice)
- Whistle register – beyond F6 (rare, used by singers like Mariah Carey)
Knowing your range helps you choose songs that fit your voice and avoid strain.
Essential Singing Techniques to Improve Range
1. Warm Up Before Singing
- Use lip trills, humming, or gentle sirens.
- Start in your mid-range and gradually move higher and lower.
- Benefits: protects your vocal cords and prepares them for flexibility.
2. Learn Your Registers
- Chest voice: your speaking register, strong and rich.
- Head voice: lighter, higher register.
- Falsetto: airy tones above chest voice.
- Whistle register: extreme high notes, rare and difficult to control.
Good singers blend registers smoothly, so transitions between low and high notes feel seamless.
3. Focus on Breath Support
- Use your diaphragm to push air steadily.
- Practice holding long notes without strain.
- Strong breath support prevents your voice from cracking on high notes.
4. Train Resonance and Placement
- Relax your throat and focus sound forward (mask resonance).
- Vowel modification—slightly adjusting vowels at higher pitches—helps maintain tone clarity.
5. Practice Range-Building Exercises
- Scales and sirens: Slide from low to high notes on “ah” or “oo.”
- Octave jumps: Sing a low note, then leap an octave higher.
- Vowel shifts: Transition from “ee” to “ah” as you climb scales.
Practical Vocal Range Chart
| Voice Type | Typical Range (approx.) | Notes Example |
|---|---|---|
| Bass | E2 – E4 | Low male voices |
| Tenor | B2 – A4 | High male voices |
| Alto | F3 – F5 | Lower female voices |
| Soprano | C4 – C6+ | Highest female voices |
use a live vocal range calculator for choir placement
Why Technique Matters More Than Range
A wide range is impressive, but control, tone, and expression are what make a singer stand out. Expanding your range without proper technique can cause strain or even damage. The best approach is to focus on:
- Smooth register transitions
- Clear tone quality
- Consistent breath control
- Emotional delivery
FAQs
How can I find my vocal range?
Use a piano, keyboard app, or free online vocal range test. Sing from your lowest note to your highest without straining.
Can anyone increase their vocal range?
Yes, with consistent training most singers can add 1–2 octaves safely.
What’s the fastest way to improve high notes?
Strengthen breath support and learn to lighten tone in your head voice.
Are whistle notes part of everyone’s range?
No, whistle register is rare and not necessary for most singers.
What’s more important, vocal range or technique?
Technique. A singer with a smaller range but great tone and control often sounds better than someone forcing extreme notes.
