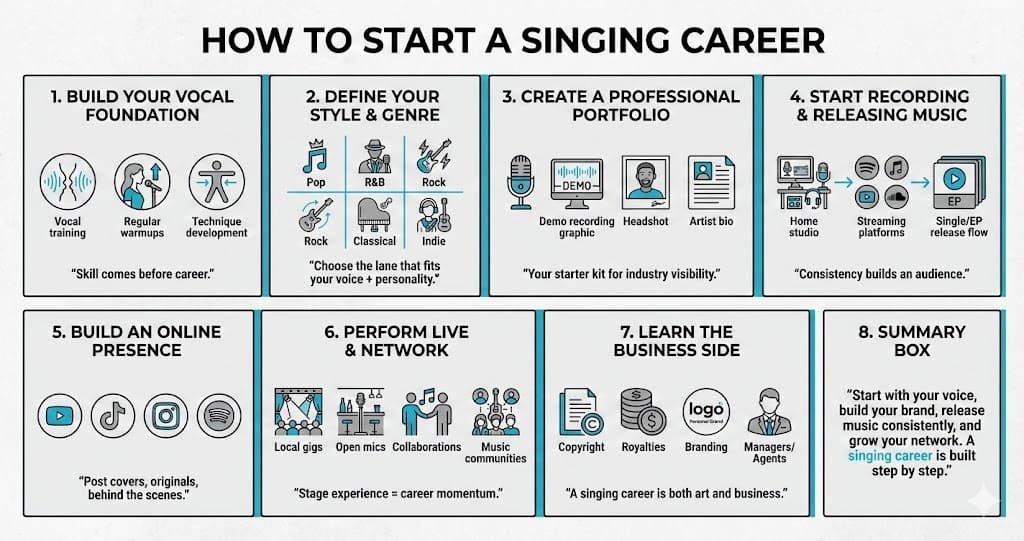
Starting a singing career is no longer limited to people with industry connections or expensive equipment. Today, singers can build careers from their bedrooms and gain millions of listeners online. But succeeding requires more than talent—it takes strategy, training, branding, consistency, and understanding how the modern music industry works.
This comprehensive guide breaks down every stage of becoming a singer, from developing your voice to releasing music, growing your audience, earning income, and building a professional career.
Understand Your Voice: The Foundation of a Singing Career
Your singing career begins with your natural instrument—your voice.
Identify Your Vocal Profile
Understanding your voice gives direction to your training and genre:
- Soprano
- Mezzo-soprano
- Alto
- Tenor
- Baritone
- Bass
A vocal range test and feedback from a coach help you map your strengths.
Master Core Vocal Techniques
Professional singers must build:
- Breath support using the diaphragm
- Resonance and sound placement
- Pitch accuracy
- Vocal agility
- Smooth register transitions (chest → mix → head)
- Dynamic control (soft vs powerful singing)
Even 10–15 minutes of structured daily practice builds long-term growth.
Train Like a Professional Vocal Athlete
Your voice is a physical instrument that requires conditioning.
Daily Practice Structure
A sustainable pro-level routine:
- Warm-up: 5 minutes (lip trills, sirens, humming)
- Technique drills: 10 minutes (scales, resonance, mix training)
- Song work: 10–20 minutes
- Cool-down: 2–3 minutes
Protect Your Vocal Health
Avoid:
- Pushing high notes
- Singing when sick
- Excessive throat clearing
- Poor hydration
Adopt healthy habits:
- Drink warm water frequently
- Do steam inhalation
- Get proper sleep
- Use mics during long rehearsals
A damaged voice can delay your career for months—prevention is part of professionalism.
If you’re looking to sing songs comfortably within your range, begin by identifying the correct key using the song key finder. Once the song fits your tessitura, check your vocal category with the voice type test for further clarity. You can monitor your technical growth with the structured vocal range improvement plan and maintain healthy habits with vocal health tips for singers.
Choose Your Musical Direction
Great singers aren’t generalists—they know who they are artistically.
Define Your Lane
Your style is shaped by:
- Vocal tone
- Musical influences
- Personality
- Message or storytelling style
- Emotional energy
Examples of artistic lanes:
- Pop vocalist
- R&B storyteller
- Indie acoustic artist
- Rock/metal vocalist
- Jazz/classical singer
- EDM/featured vocalist
Find Your Unique Selling Point (USP)
You need a reason people will remember you:
- Unusual tone
- Impressive range
- Distinct look or personality
- Strong emotional delivery
- A signature genre blend
Most successful singers create a recognizable sound early on.
Build a Professional Artist Brand
Branding is what transforms a good singer into a memorable artist.
Develop Key Brand Elements
- Stage name
- Visual identity (colors, styling, photography style)
- Brand voice/personality
- Genre and target audience
- Story behind your artistry
Craft Your “Artist Origin Story”
This narrative should answer:
- Who are you?
- What makes your story unique?
- Why do you make music?
- What do you want listeners to feel?
Your story builds emotional connection—essential for building a loyal fanbase.
Learn Music Skills That Elevate Your Career
You don’t need to be a musical genius, but you must understand:
The Essentials
- Basic music theory
- Rhythm control
- Ear training
- Understanding harmonies
- Songwriting fundamentals
- Basic piano or guitar
These skills help with:
- Recording
- Collaborating with producers
- Songwriting
- Live performance
The more skills you have, the more opportunities you unlock.
Build Your First Recording Setup
You can start with a simple, budget-friendly home studio that still sounds professional.
Essential Equipment
- USB microphone (beginner) or XLR mic + audio interface (intermediate)
- Pop filter
- Closed-back headphones
- Acoustic treatment or DIY blankets
- DAW (GarageBand, FL Studio, Logic Pro, Ableton)
What to Record First
- At least 2–3 cover songs
- A simple vocal showcase
- A short demo (30–60 seconds)
- Your first original song if possible
Your early recordings represent your artistic identity—invest effort into quality.
Release Music Like a Modern Independent Artist
Today, singers don’t wait for labels—they self-release.
Distribution Platforms
- DistroKid
- TuneCore
- CD Baby
- Amuse
Release Strategy for a Beginner
- Pick one high-quality original track
- Create 20–30 short promo clips for TikTok/Reels
- Tease the song weekly before release
- Drop a lyric video or live version soon after
- Submit to playlists and curators
The first 90 days of releasing music matter more than the song’s budget.
Grow Your Audience Online
Success today is determined by visibility—not gatekeepers.
Best Platforms for Singers
- YouTube (covers, live sessions, storytelling)
- TikTok (short performances, personality clips)
- Instagram (visual branding, reels, behind-the-scenes)
- Spotify (original music releases)
- SoundCloud (early demos)
Content That Drives Growth
- High-quality covers of trending songs
- “Before and after” vocal transformation clips
- Duets and singing challenges
- Studio session clips
- A cappella or stripped-down versions
Consistency beats perfection—post weekly, improve monthly.
Start Performing and Building Real-World Experience
Performing live builds confidence, stage presence, and credibility.
Where Beginners Can Perform
- Open mic nights
- Community events
- Talent shows
- Cafés and small venues
- School/college events
- Busking (street performance)
- Private events (weddings, parties)
Benefits of Live Performance
- Real-time audience feedback
- Networking opportunities
- Experience working with sound equipment
- Building stage confidence
- Exposure to potential fans
Live performance separates real artists from hobbyists.
Network with Industry Professionals
The music industry is built on relationships.
Important Connections
- Producers
- Engineers
- Songwriters
- Videographers
- Managers
- PR specialists
- Other singers
Networking expands your opportunities more than talent alone.
How to Network Effectively
- Attend open mics and music events
- Join online music communities
- Reach out for collaborations
- Engage consistently on social media
- Be professional and reliable
Professionalism builds a long-term career faster than talent without discipline.
Learn How Singers Actually Make Money
A real singing career includes multiple income streams.
Main Revenue Sources
- Streaming royalties
- YouTube monetization
- Live performance fees
- Brand deals and sponsorships
- Merchandise
- Patreon or membership platforms
- Music licensing (TV, film, ads)
- Session singing/vocal features
- Teaching or vocal coaching
Diversifying your income makes your career sustainable.
Choose Your Career Path: Independent vs Label
Independent Artist Advantages
- Total artistic control
- Ownership of masters
- Flexible release schedule
- Higher revenue share
Record Label Advantages
- Marketing and PR support
- Professional production
- Tour funding
- Bigger exposure
Both routes can work—what matters is your goals, resources, and long-term vision.
Build a Professional Career Roadmap
A sustainable singing career develops in stages.
Career Timeline Framework
Stage 1: Development (3–12 months)
Voice training, covers, brand building, content creation
Stage 2: Early Career (1–3 years)
First releases, small performances, audience building
Stage 3: Breakthrough (3–5 years)
Viral content, collaborations, touring, monetization
Stage 4: Professional Artist (5+ years)
Established fanbase, consistent income, brand partnerships
The more strategic your roadmap, the faster your career will grow.
Common Mistakes That Stop Singers from Succeeding
- Waiting for perfection
- Comparing yourself to other artists
- Inconsistent posting
- Avoiding investment in skills or equipment
- Relying on raw talent without training
- Ignoring branding
- Not learning basic music business
- Expecting overnight success
Avoid these errors and you’ll progress twice as fast.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I start a singing career with no experience?
Yes. Many successful singers started from scratch by training daily and posting consistent content.
What age is best to start a singing career?
Any age. The industry now embraces teenagers, adults, and even older beginners.
Do I need a vocal coach?
Not mandatory but extremely beneficial for faster progress and vocal safety.
How long does it take to become a professional singer?
Typically 1–5 years depending on consistency, training, and content strategy.
Do I need a lot of money to start?
No. Beginners can start with basic equipment and free distribution tools.
Conclusion
Starting a singing career today requires more than just a great voice—it’s a combination of training, strategy, branding, consistent content, and industry knowledge. With modern tools and platforms, any dedicated singer can build a successful career from the ground up.
